As the world embraces sustainable energy solutions, lithium batteries have emerged as a game-changer in the realm of recreational vehicles (RVs), marine vessels, and golf carts. These high-performance batteries offer longer lifespan, faster charging times, and lighter weight compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. However, to maximize their efficiency and lifespan, proper maintenance is crucial.
In this article, we'll delve into the essential tips for maintaining lithium batteries in RVs, marine vehicles, and golf carts, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
What is A LFP Battery
An LFP battery is a type of lithium-ion battery that uses lithium iron phosphate as the cathode material. LFP stands for "lithium iron phosphate," which is the chemical compound used in the battery's cathode. This type of lithium-ion battery is known for its high energy density, long cycle life, and enhanced safety features.
LFP batteries have gained popularity in various applications due to their stable chemistry, thermal stability, and resistance to thermal runaway, making them a safer option compared to other lithium-ion batteries. They are commonly used in electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy storage systems, backup power systems, and other applications where high energy density and long life are essential.
Key advantages of LFP batteries include:
1. Safety: LFP batteries are considered safer than other lithium-ion batteries due to their stable chemistry and resistance to thermal runaway, making them less prone to overheating and combustion.
2. Long Cycle Life: LFP batteries can withstand a high number of charge-discharge cycles, making them suitable for applications where durability and longevity are crucial.
3. High Energy Density: LFP batteries offer high energy density, allowing them to store a significant amount of energy in a compact space, making them suitable for use in electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
4. Fast Charging: LFP batteries can be charged at a faster rate compared to some other lithium-ion batteries, making them ideal for applications requiring rapid charging capabilities.
5. Environmental Friendliness: Lithium iron phosphate is considered more environmentally friendly compared to other lithium-ion battery chemistries, as it contains no cobalt, which is associated with environmental and ethical concerns in mining.
Due to these advantages, LFP batteries have become a popular choice for various energy storage and mobile power applications, offering a balance of performance, safety, and longevity.
Suggest reading: AGM Vs. Lithium Batteries: Which Is Better For RV And Marine

LiTime 12V 100Ah Group 24
Maintaining the Longevity of Rechargeable Lithium Iron Batteries
Rechargeable lithium iron batteries have a limited lifespan and will gradually lose their ability to retain a charge over time. Once a battery has depleted its capacity, this deterioration is irreversible. Therefore, it is crucial to properly maintain and care for your lithium battery.
1.Inspect the Battery Condition Regularly
The estimated lifespan of a lithium iron battery ranges from 10 to 15 years, depending on its usage. LiTime LiFePO4 batteries can endure up to 4000 complete charging cycles or as many as 15000 partial cycles. A complete charging cycle involves using the battery from full charge to full discharge and then fully recharging it. Allowing your batteries to remain unused for extended periods can impede their lifespan and potentially lead to battery failure if left unattended for too long.
LiTime advise that all lithium batteries and cells not in use undergo at least one full maintenance cycle (charge to 100% state of charge, discharge to 100% depth of discharge, charge to 50% state of charge) once every 6-12 months to preserve the battery's capacity. Please verify that batteries and cells in storage maintain an adequate open circuit voltage (OCV). Refer to the table below to determine the minimum recommended voltage for storage. If, during your maintenance check, the voltage falls below this value, LiTime recommends recharging your battery to the upper end of the voltage ranges provided below.
|
Voltage Range (v)
|
Battery System
|
|
3.3-3.4
|
Individual cell
|
|
13.2-13.6
|
12V Battery
|
|
26.4-27.2
|
24v Battery
|
|
39.6-40.8
|
36V Battery
|
|
52.8-54.4
|
48V Battery
|
When conducting semi-annual voltage checks on cells or batteries, ensure to examine for terminal corrosion and the integrity of the casing. Do not utilize any battery or cell that displays signs of damage.
Regardless of how well you maintain and store your battery, LiFePO4 batteries will continue to slowly self-discharge while in storage and not in use, around 1%-3% per month which is much lower than lead acid batteries. If your battery incorporates features like Bluetooth, the self-discharge rate will be higher due to the draw of the Bluetooth module. Regularly monitoring your battery's charge will help maintain its health and enhance its energy output for your specific application.
A simple at-home method to assess the battery's condition is to monitor the run-time of your application. Upon purchasing your new lithium battery, take note of the initial run time it provides for your application. This initial run time will serve as a benchmark for comparison as your battery ages, allowing you to gauge its health. The run time will vary based on the application and configuration you are running.
2.Charge The Battery Properly
A lithium-specific battery charger is the ideal choice for ensuring a complete charging cycle each time. LiTime LiFePO4 battery chargers are equipped with an intelligent 3-step charging logic designed to effectively charge even deeply discharged batteries. Furthermore, to optimize battery performance and lifespan, our advanced charging technology maximizes the battery capacities during charging.
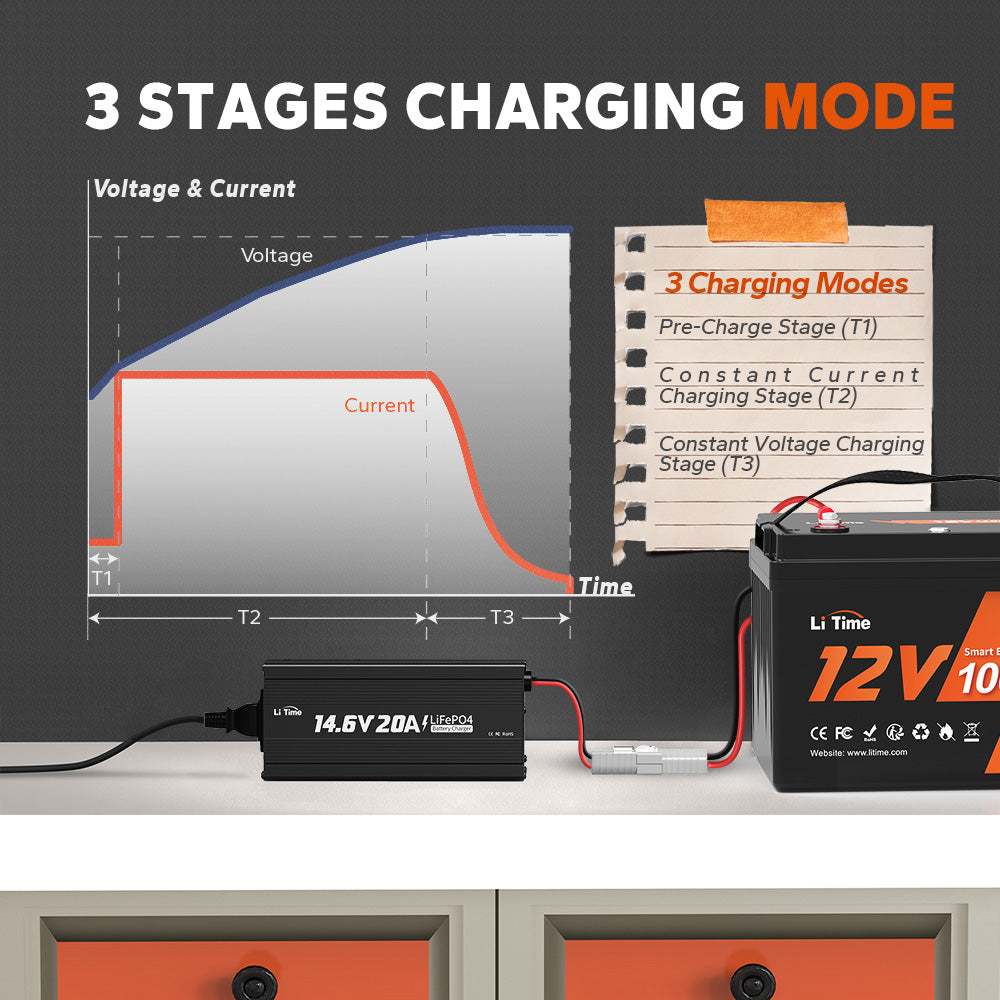
When it comes to extending the life of a lithium battery, the charging rate is crucial. Chargers are chosen based on a fraction of the battery's capacity. For instance, a lithium battery can be charged at a rate as fast as 1C (equivalent to the capacity of the battery), while a lead acid battery should be charged at a rate below C/3 (one-third of the battery's capacity). This means that a 10Ah lithium battery can be charged at 10 amps, whereas a 10Ah lead acid battery should be charged at about 3 amps.
To maximize the life of a lithium battery while ensuring fast charging to minimize downtime, we recommend charging your LiFePO4 battery at 0.2C but no faster than 0.5C. In the case of a 100Ah battery, this translates to a charge rate of 20A to 50A, with 20A being the optimal choice. For instance, if you were considering chargers and had the option of a 20A charger or a 50A charger, we would advise selecting the 20A charger. While the 50A charger may take around 2 hours to charge, it could potentially shorten the battery's lifespan. On the other hand, the 20A charger may take approximately 5 hours to charge but will maximize the battery's lifespan.
Besides, charging the battery with proper voltage is essential, here’s the charging voltage that LiTime recommends.

Charging the battery below freezing point is not a good idea. If you are in the area where the winter is long, battery with low-temperature charging-off protection and self-heating function is important. Visit LiTime cold-weather series for winter guard.
3. Store the Battery Well
When storing batteries for an extended period, it's important to note that the storage requirements differ for SLA and lithium batteries.
The optimal state of charge (SoC) for storage is determined by the battery's chemistry. For SLA batteries, it's best to store them as close to 100% SoC as possible to prevent sulfating, which leads to the accumulation of sulfate crystals on the lead plates and reduces battery capacity. In contrast, lithium batteries should be stored at around 50% SoC to maintain stability in the positive terminal and prevent permanent capacity loss. For detailed recommendations on long-term lithium storage, refer to this guide on storing lithium batteries.
Another factor to consider is the self-discharge rate. SLA batteries have a high self-discharge rate, so it's advisable to keep them on a float or trickle charge to maintain them near 100% SoC and prevent sulfation and permanent capacity loss. On the other hand, lithium batteries, with their lower discharge rate, may require minimal maintenance charging if there are no parasitic draws on the battery, such as a Bluetooth module.
Bonus Tip: Keeping the Battery Away from Terminal Corrosion
Lithium batteries, such as lithium-ion and lithium polymer batteries, are generally less prone to terminal corrosion compared to traditional lead-acid batteries. This is because lithium batteries use different chemistries and materials that are less susceptible to the types of corrosion commonly seen in lead-acid batteries.
However, while lithium batteries are more resistant to corrosion, they are not completely immune to all forms of degradation. It's important to note that lithium batteries can still experience issues related to their terminals, albeit to a lesser extent. Factors such as exposure to moisture, extreme temperatures, and physical damage can still impact the terminals and connections of lithium batteries.
So follow these 2 rules can minimize the possibility of lithium batteries’ terminal corrosion:
- Storing your battery in a cool and dry environment is a simple method to minimize corrosion. Not only does this reduce corrosion, but it also extends the battery's shelf life and overall lifespan. To prevent corrosion effectively, consider sealing your terminals using a spray-on protectant, which is commonly found in most auto parts stores.
- Regularly inspecting your lithium battery terminals for dirt and cleaning them with a soft, dry cloth before use will prevent the accumulation of a substantial buildup that could become challenging to remove later on.
While the risk of terminal corrosion is lower with lithium batteries, it's always a good idea to follow best practices for battery maintenance to maximize their lifespan and performance.
Conclusion
Lithium batteries have revolutionized the power storage industry, offering unparalleled performance and efficiency. By adhering to these maintenance practices, owners of RVs, marine vessels, and golf carts can ensure that their lithium batteries continue to deliver reliable power for years to come. Proper charging, temperature management, regular inspections, correct installation, and monitoring the Battery Management System are all integral parts of maintaining lithium batteries.
By following these guidelines, enthusiasts can maximize the potential of their lithium batteries, enhancing their overall experience with their recreational vehicles and equipment.

Classic
Bluetooth
Low-Temp
Self-Heating
2C-Rate
Classic
Starting
Low-Temp
Bluetooth
Self-Heating
2C-Rate
Bluetooth
Low-Temp
Self-Heating
Classic
Low-Temp
Bluetooth
2C-Rate
Low-Temp
Bluetooth
2C-Rate
Classic
Low-Temp
Bluetooth
2C-Rate
Waterproof
Multi-Bank
Bluetooth
Waterproof
Classic
Low-Temp
Bluetooth
Self-Heating
Starting
2C-Rate



































































































































